SPINAL PROBLEMS

The main cause of spinal problems is due to dysfunction of one or more structures of the Human Spine: Mainly the Discs, Ligaments, Muscles, Joints, Nerves & Bones.
Various spinal problems classification:
Degenerative Conditions
Slip Disc:
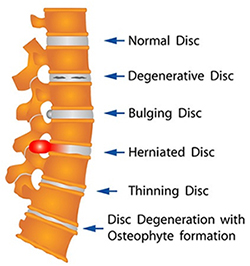
A disc is the soft gelatinous structure between the two bones in the spine. The disc acts like a “shock absorber” (absorbing the weight of the body during movements) and preventing the bones touching one other.
[Figure showing normal disc ]
The height of the disc depends on the amount of internal soft gelatinous core, and is mostly normal in healthy individuals under the age of 20.
Either due to improper Posture or imperfect lifestyle and also due to Aging, the soft Disc in all individuals loses its elasticity due to changes in the internal core. As the elasticity decreases, the constant body pressure causes the disc height to decrease.
[ Figure of spine with discs in various stages of degeneration]
The reduction in disc heights leads to the bones (vertebra) coming close to each other. This condition is known as ‘degenerated disc’. This leads to onset of back pain and stiffness.
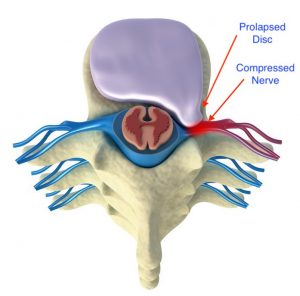
In a degenerated/damaged disc when the inner jelly core bulges out through the exterior, it is called as ‘slip disc’ or ‘prolapsed disc’.
[ Figure showing prolapsed / slipped disc]
This disc material presses on the nerves that are behind the disc.
This leads to “inflammation” or internal swelling of the nerves, causing symptoms of leg pain or arm pain starting from the back or neck and going down.
[ Figure showing slipped disc pressing on the nerve]
If the Inflammation increases it leads to numbness/altered sensation and later on can lead to weakness in hands and legs.
![MRI Picture of Slip Disc]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Sd-1-119x300.jpeg)
![MRI Picture of Slip Disc]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Sd-2-215x300.jpeg)
[ MRI Picture of Slip Disc]
Spinal stenosis is the compression of the spinal cord and nerves due to either
- Increase in thickness of ligaments surrounding the nerves.
[Figure showing normal spinal canal and spinal canal compressed due to artritis and increase thickness]
Arthritis of joints (increase in bony structures) .
or severe disc prolapse
[Figure showing comparison between normal and stenotic spinal canal ]
Spinal stenosis is more commonly associated with advancing age and sedentary lifestyles. As the body naturally ages it leads to changes in the structures surrounding the spinal nerves. Early insignificant significant changes without severe spinal cord compression are called as spondylosis.![comparision between normal spine & stenotic spine]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/112249095_s-1-300x279.jpg)
[Figure showing stenosis causing compresion of nerve ]
Initially Spondylosis does not cause any major problems, except maybe occasional back/neck pain,
But as the aging and degeneration progress (and in some people more rapidly then others),
it leads to frequent complaints of back or neck pain in getting up,
stiffness in turning in bed ,
mainly Numbness or tingling in both legs/arms,
associated with pain or heaviness in arms or feet starts developing.
This can lead to walking disturbances, slipping of slippers from feet, loss of power in arms or weakness in holding objects.
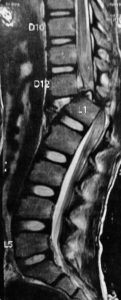
Advanced stage of compression of the spinal cord can also cause bowel or bladder problems like constipation or urinary hesitancy, and their canoe wasting or thinning of the arms or legs due to chronic compression.![. [MRI picture of stenosis in lumbar spine]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/ss-5-225x300.jpeg)
![[MRI picture of stenosis in lumbar spine]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/ss-6-189x300.jpeg)
[MRI picture of stenosis in lumbar spine]
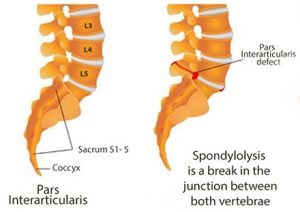
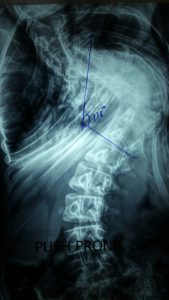
“Spondylolysis” means a fracture or defect in the posterior portion of the vertebra, leading to bony discontinuity between the anterior and posterior parts.
[Figure showing spondylolysis]
Any discontinuity causes instability between adjoining 2 vertebra .
[Figure showing Spondylolysthesis]
This instability causes abnormal movement of one vertebra over the other. As one vertebral body slips over the other it narrows the opening of the nerves- situated behind.
Slipping of one vertebra over another usually occurs only during movements, thus the opening of the nerves get more narrowed then leading to compression of the nerves.
This compression leads to inflammation of the nerves leading to symptoms of radiating or shooting pain in the legs and eventually numbness and heaviness in the legs.
“Spondylolisthesis” means a permanent slip of one vertebra over another. It may occur due to spondylolysis or due to spinal stenosis.
[Figure explaing how spondilolysis progress to spondylolisthesis]
A spondylolysis if it is present very early since birth, or the result of a trauma, the slip becomes permanent, thus one vertebra is permanently displaced anteriorly leading to continuous narrowing of the nerve opening.
In some cases of spinal stenosis as discussed earlier, there is excess growth around the bones and surrounding tissues also tend to become thicker. This excess growth is called arthritis of the joints and leads to hyper mobility over these joints. This movement in turn leads to one vertebra constantly shifted anterior in respect to the other.
This permanent slippage means there is a constant pressure over the nerves, causing continuous inflammation, which subsides and again increases, this over time can lead to nerve damage if not rectified.
[MRI pic showing spondylolysthesis]
A nerve damage that happens due to constant pressure causes spasms and tightness in the muscles-that the nerve supplies-which over Time can cause wasting and thinning of the muscles.
Thus Spondylolisthesis and Spinal Stenosis in the long term can lead to irreversible changes in the functioning of the nerves leading to symptoms of muscle wasting and muscle cramps.
Infective
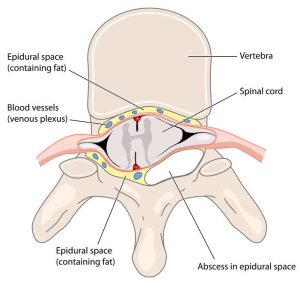
Tb infection is among the most common infections affecting the Indian population. After the lungs, the spinal column among the bones is the most common site that can be affected by Tb. Tuberculous infection of the spine can be very devastating if not diagnosed at the right time. Tb of the spine causes destruction of the bones and leads to pus formation called ‘abscess’. This abscess can cause compression of the spinal cord leading to damage of the nerves.
Figure showing abscess compressing the spinal cord
If diagnosed early then proper medications prevents the spread of the pus and also helps in recovery of the damaged vertebral bone. Most of the times only medications are enough to cure these infections.
Figure MRI picture showing the abscess with bony destruction
Nowadays it is very important to get a Biopsy from the affected bone to determine not only if it is Tb, but also what variant of Tb and what line of medications will be effective against it. In early cases a Biopsy and proper medications along with bracing is effective in treating the infection.
If left diagnosed or due to late diagnosis the patient can develop severe pain and also weakness in the legs or arms. This happens when the abscess and bony destruction increases and progresses leading to compression and damage of the spinal cord.
In such cases a surgical decompression of the spinal cord is required, along with decompression, stabilization of the spine is also required as the bony destruction leads to instability. Nowadays , this procedure is done by us through a minimally invasive approach, so as to reduce the morbidity of the procedure and the patient can be rehabilitated early.
Congenital / Acquired
Deformity of the spine in the front back or anteroposterior view is known as scoliosis. Scoliosis is either present at birth or can start 5-8 years after birth.
If its present at birth usually the scoliosis can worsen rapidly, and by the time the child turns 8-10 the deformity is very severe and can cause restriction of breathing and other problems also.
Figure showing depicting the scoliosis curves as seen in young adults
An abnormal curvature of the spine in side profile, is called kyphosis.
Kyphosis can be present since birth, or it can develop in later stages.

If it develops after birth then it can be due to various factors like trauma, infections or in older population due to weak bones condition called osteoporosis.
In infections like Tb, as discussed earlier if the infection is resolved by medicines the bony healing always does not happen in normal natural way, and an abnormal growth can lead to kyphosis development.
Figure showing development of kyphosis due to abnormal bony development after tuberculosis treatment
Most of the deformities are only cosmetically unappealing without any major neurological or clinical symptoms, and for a smaller scoliosis/ kyphosis usually we can manage by bracing and exercises only without any major intervention
Only if the deformities start causing neurological symptoms or they cause severe deformity with pain , then the deformities are aggressively tackled by a surgical intervention.
The deformities which are present at birth can cause additional neurological symptoms like weakness in the legs, bowel or bladder disturbances, thus it becomes necessary to correct these deformities as soon as possible after birth, so as to prevent these neurological symptoms from progressing.
Surgical correction is also required if we anticipate cardiac or respiratory problems to worsen, as in these deformities if the curvature increases it can lead to compression of the lungs or heart.
In children where the deformity is only cosmetically unappealing, it is necessary to monitor the curve serially, any sudden increase in the deformity as the age increases necessitates a surgical correction.
Figure showing the change in curve growth as age progresses
Sometimes these deformities develop in adults after the age 50/60. These especially happen due to osteoporosis or due to severe spinal stenosis with instability, these conditions which develop in adulthood are sometimes called as adult kyphoscoliosis or adult degenerative kyphoscoliosis.
The later development of these deformities, makes them very rigid/stiff but the bone quality can be very poor due to osteoporosis, thus correction of the spine in this age group is challenging.

Figure showing the progress of scoliosis in adults leading to neural compression & deformnity.
Nowadays, we can attempt to correct these deformities through multiple minimally invasive approaches, so that the trauma and post-operative pain to the patient is less.
AutoImmune Inflammatory / Bone Related
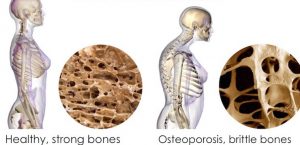
Osteoporosis means decrease in the bone density, this generally occurs in old age, when there is loss of calcium and essential elements from the bones, this causes weakening of the bony framework, leading to decrease in bony density.
Figure 1 showing how the bone becomes brittle due to loss of material.
The bones most commonly affected by Osteoporosis are those of the spinal column, the hip bones and the forearms.
Osteoporosis is also most commonly seen in females compared to male population, especially in Indian Females there is a greater tendency, it can occur commonly in Postmenopausal ladies, Post hysterectomy ladies and also in people affected by Diabetes and Kidney Problems for a longer duration.
The addition of early hysterectomy to postmenopausal ladies increase the risk of osteoporosis by almost 50% compared to normal postmenopausal ladies.
People with long standing Diabetes or Thyroid disorders, also individuals having rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to develop Osteoporosis, the reason being the calcium and essential bony minerals depletion is very rapid compared to their deposition, this creates a negative balance and causes weakening of the bony framework.
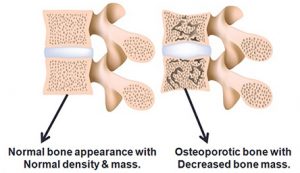
Osteoporosis figure showing weak spinal bones with loss of bony matrix.
Weakness of the spinal bones leads to inability of the bones to bear the the body weight, especially in cases of trivial fall or slip.
Thus people with weak bones get a fracture very easily even with a trivial fall. These bones once fractured take a long time to heal as the bones are hollow and have extensive loss of bony framework and additional loss of essential bone building materials. Apart from the pain and discomfort associated with slow healing, the mobility is also hampered.
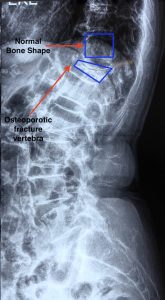
Figure showing osteoporosis fracture showing compression of bones and change in spinal curvature.
Many of the individuals who suffer an osteoporotic fracture are either above the age of 65, or may have other medical problems, thus if mobility is restricted, chances of some other medical problem escalating is very high.
Thus it is very essential to diagnose osteoporosis early and treat it appropriately with proper medications and diet supplementation and exercises.
Treatment of Osteoporosis Fractures involves a Minimally Invasive procedure called Vertebroplatsy / Kyphoplasty. In this procedure we inject bone cement into the fractured bone and prevent its further collapse.
Some autoimmune inflammatory conditions of the spine cause inflammation of the joints present between two vertebra. This internal inflammation leads to bony surfaces being jammed against each other leading to less free space between the bones. This leads to stiffness and restricted movement across the joints.
The inflammation reduces by medications but repeated inflammation leads to destruction of the lining of these joints.
Due to such autoimmune inflammatory conditions, many joints are affected but most commonly affected are the weight bearing joints like those of the back, the hip, knee & shoulders. It starts with light pain and stiffness and gradually progresses to restriction in day to day activities also.
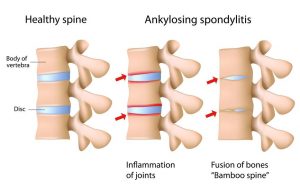
In extreme type of inflammatory arthritis like (ankylosing spondylitis), the joints start getting fused with each other, leading to permanent restriction of mobility and stiffness , the spine becomes like a bamboo, without any flexibility.
Figure showing how the joint between spinal bones progress from inflammation to complete fusion.
The most common auto-immune conditions seen are Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic arthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis and Gouty Arthritis.
The solution usually is early diagnosis and treatment with proper medications and physiotherapy.
Only If the person comes with an advanced stage of deformity, and the deformity is actively affecting his lifestyle then a deformity correction spinal surgery is necessary to prevent further worsening of deformity.
Tumors
Tumours of the Spine may arise primarily from spinal elements, or they may be secondary to a tumour elsewhere in the body which can spread (metastatise) to the spinal cord.
Tumors which originate from the Spine primarily, can be benign or can be Malignant.
The diagnosis of tumours is done by doing a PET scan, along with an MRI. The PET scan gives an idea where is the spread and origin of the tumour from.
A biopsy from the affected spinal vertebra tells us what type of tumour is it.
Benign Tumors are slow growing, rarely become aggressive or malignant, and most of the times do not cause any neural compression. Most of these tumours do not require any surgical intervention and can be just managed conservatively by observing them periodically.
Some Benign and mostly all Malignant and metatstatic tumours present with symptoms of vertebral body destruction, and neural compression leading to symptoms of pain , disability and severe neural deficits. 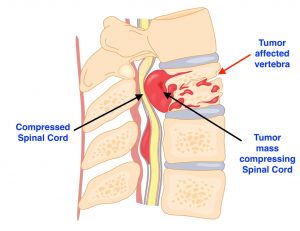
Figure showing tumour affecting the vertebral body leading to destruction and compression on the spinal cord.
In Malignant and some Benign tumours there is the need for a radical surgical intervention, while in some metastatic cases it may be that only a palliative surgery is offered.
The type of surgery is decided by Our team based on the various reports and patient profile.
Trauma
Spinal fractures can occur either due to high velocity vehicular accident or fall from height or assault.
Usually the trauma causes bony compression without any major injury to the spinal cord.
Figure showing various types of frat tubes commonly seen.
In some cases the injury is of high intensity and there is major destruction or damage of the bone,
Figure showing displacement of the bones due to high velocity injury.
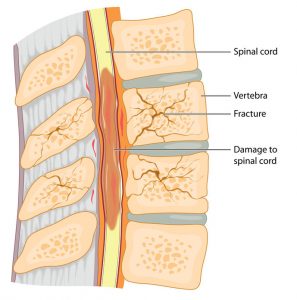
This leads to compression of the spinal cord behind the bones, leading to inflammation and internal damage of the nerves, due to this severe compression.
Figures showing bony injury with spinal cord compression and nerve damage.
Nerve damage can lead to partial or complete paralysis and can also affect the functioning of other vital organs like bowel & bladder function & respiration.
If this compression is not relieved immediately then the neural damage can worsen and remain permanent. It can even lead to permanent paralysis ( called paraplegia or quadriplegia) ,
We need to decompress the spine and stabilise it with implants like rods screws/plates so that the spine is supported and stable. Many of the spinal surgeries for fracture treatment can be done in a minimally invasive technique also.




![[ Figure showing slipped disc pressing on the nerve] [ Figure showing slipped disc pressing on the nerve]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/slip-disc-275x300.jpg)
![Figure showing normal spinal canal and spinal canal compressed due to artritis and increase thickness]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/s-s-3-229x300.jpg)

![[Figure showing comparison between normal and stenotic spinal canal ]](http://advancedspinecare.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/s-s-2-212x300.jpg)